|
|
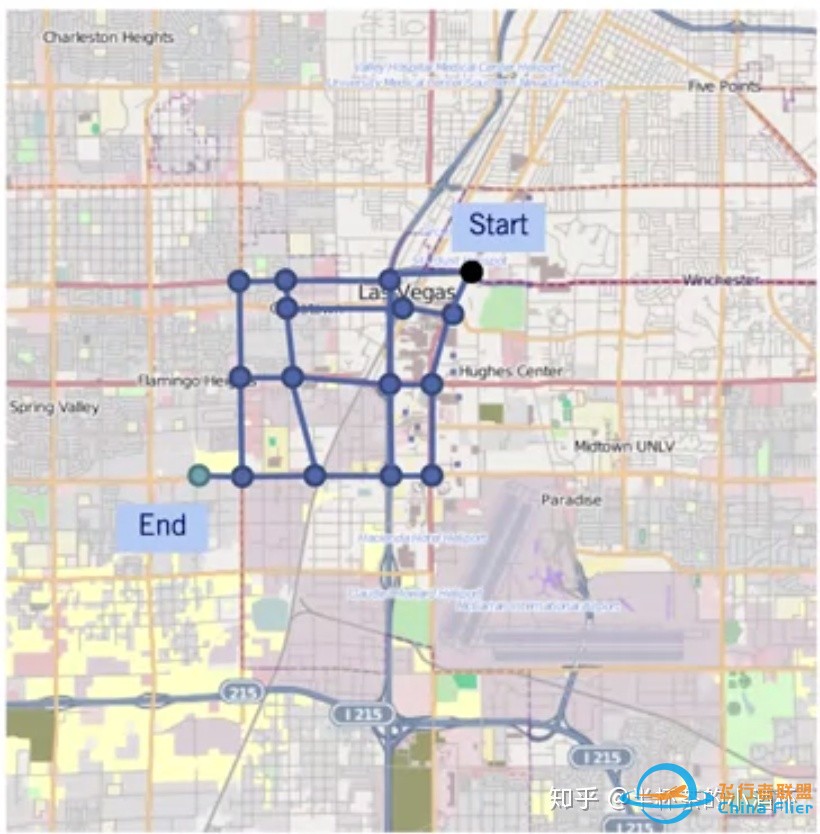
自动驾驶运动规划(Motion Planning)中提到Mission Planner关注High-Level的地图级别的规划,通过Graph Based的图搜索算法实现自动驾驶路径的规划。今天看看如何用Python实现Graph Based的BFS最短路径规划。
1、Graph的基础定义及Python表达
在数学或者计算机数据结构的教材中,Graph由Node(或者vertices)组成,Node之间以Edge连接(如下图所示)。如果Node之间的连接是没有方向的,则称该Graph为无向图(Undirected Graph);反之,如果Node之间的连接是有方向的,则称为该Graph为有向图(Directed Graph);有向图(Directed Graph)的Edge被成为Arc。
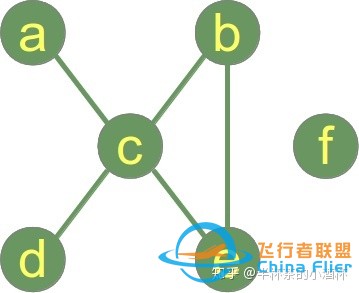
上图的Graph在Python中可以借助Dictionary表达:
graph = { "a" : ["c"],
"b" : ["c", "e"],
"c" : ["a", "b", "d", "e"],
"d" : ["c"],
"e" : ["c", "b"],
"f" : []
}Graph的Edge可以用tuple表达,比如连接a和b的Edge可以表示为(a, b)。我们可以实现一个从Graph生成Edge的函数。
def generate_edges(graph):
edges = []
for node in graph:
for neighbour in graph[node]:
edges.append((node, neighbour))
return edges
print(generate_edges(graph))generate_edges()函数生成Graph的所有Edge:
[('a', 'c'), ('c', 'a'), ('c', 'b'), ('c', 'd'), ('c', 'e'), ('b', 'c'), ('b', 'e'), ('e', 'c'), ('e', 'b'), ('d', 'c')]可以看到,由于Node f是孤立节点,所有所有Edge中都不包含Node f。
2、Python实现基础Graph类
在了解Graph的基础概念之后,用Python实现一个Graph类。
""" A Python Class
A simple Python graph class, demonstrating the essential
facts and functionalities of graphs.
"""
class Graph(object):
def __init__(self, graph_dict=None):
""" initializes a graph object
If no dictionary or None is given,
an empty dictionary will be used
"""
if graph_dict == None:
graph_dict = {}
self.__graph_dict = graph_dict
def vertices(self):
""" returns the vertices of a graph """
return list(self.__graph_dict.keys())
def edges(self):
""" returns the edges of a graph """
return self.__generate_edges()
def add_vertex(self, vertex):
""" If the vertex "vertex" is not in
self.__graph_dict, a key "vertex" with an empty
list as a value is added to the dictionary.
Otherwise nothing has to be done.
"""
if vertex not in self.__graph_dict:
self.__graph_dict[vertex] = []
def add_edge(self, edge):
""" assumes that edge is of type set, tuple or list;
between two vertices can be multiple edges!
"""
edge = set(edge)
(vertex1, vertex2) = tuple(edge)
if vertex1 in self.__graph_dict:
self.__graph_dict[vertex1].append(vertex2)
else:
self.__graph_dict[vertex1] = [vertex2]
def __generate_edges(self):
""" A static method generating the edges of the
graph "graph". Edges are represented as sets
with one (a loop back to the vertex) or two
vertices
"""
edges = []
for vertex in self.__graph_dict:
for neighbour in self.__graph_dict[vertex]:
if {neighbour, vertex} not in edges:
edges.append({vertex, neighbour})
return edges
def __str__(self):
res = "vertices: "
for k in self.__graph_dict:
res += str(k) + " "
res += "\nedges: "
for edge in self.__generate_edges():
res += str(edge) + " "
return res测试一下Graph类的实现。
if __name__ == "__main__":
g = { "a" : ["d"],
"b" : ["c"],
"c" : ["b", "c", "d", "e"],
"d" : ["a", "c"],
"e" : ["c"],
"f" : []
}
graph = Graph(g)
print("Vertices of graph:")
print(graph.vertices())
print("Edges of graph:")
print(graph.edges())
print("Add vertex:")
graph.add_vertex("z")
print("Vertices of graph:")
print(graph.vertices())
print("Add an edge:")
graph.add_edge({"a","z"})
print("Vertices of graph:")
print(graph.vertices())
print("Edges of graph:")
print(graph.edges())
print('Adding an edge {"x","y"} with new vertices:')
graph.add_edge({"x","y"})
print("Vertices of graph:")
print(graph.vertices())
print("Edges of graph:")
print(graph.edges())程序的输出如下:
Vertices of graph:
['a', 'c', 'b', 'e', 'd', 'f']
Edges of graph:
[{'a', 'd'}, {'c', 'b'}, {'c'}, {'c', 'd'}, {'c', 'e'}]
Add vertex:
Vertices of graph:
['a', 'c', 'b', 'e', 'd', 'f', 'z']
Add an edge:
Vertices of graph:
['a', 'c', 'b', 'e', 'd', 'f', 'z']
Edges of graph:
[{'a', 'd'}, {'c', 'b'}, {'c'}, {'c', 'd'}, {'c', 'e'}, {'a', 'z'}]
Adding an edge {"x","y"} with new vertices:
Vertices of graph:
['a', 'c', 'b', 'e', 'd', 'f', 'y', 'z']
Edges of graph:
[{'a', 'd'}, {'c', 'b'}, {'c'}, {'c', 'd'}, {'c', 'e'}, {'a', 'z'}, {'y', 'x'}]3、Graph中的路径查找(Path Finding)
有了Graph结构之后,我们看看如何实现查找从一个Node到另一个Node的路径的问题。在实现Python代码之前,我们再复习一些概念:
邻接节点(Adjacent Vertices):如果两个Vertices存在一条连接Edge,则称它们是相邻接的。
无向图中的Path: 无向图中的Path是一个点序列P = (v_1, v_2, ..., v_n),序列中相邻的节点都是相邻接的。
简单路径(Simple Path):没有重复节点的Path称为Simple Path。
3.1 Graph中路径查找的递归实现
实现查找一条从开始顶点(Start Vertex)到结束顶点(End Vertex)的简单路径(Simple Path) 的算法。
def find_path(self, start_vertex, end_vertex, path=None):
""" find a path from start_vertex to end_vertex
in graph """
if path == None:
path = []
graph = self.__graph_dict
path = path + [start_vertex]
if start_vertex == end_vertex:
return path
if start_vertex not in graph:
return None
for vertex in graph[start_vertex]:
if vertex not in path:
extended_path = self.find_path(vertex,
end_vertex,
path)
if extended_path:
return extended_path
return None查找从开始顶点(Start Vertex)到结束顶点(End Vertex)的所有简单路径(Simple Path)的算法。
def find_all_paths(self, start_vertex, end_vertex, path=[]):
""" find all paths from start_vertex to
end_vertex in graph """
graph = self.__graph_dict
path = path + [start_vertex]
if start_vertex == end_vertex:
return [path]
if start_vertex not in graph:
return []
paths = []
for vertex in graph[start_vertex]:
if vertex not in path:
extended_paths = self.find_all_paths(vertex,
end_vertex,
path)
for p in extended_paths:
paths.append(p)
return paths查找从开始顶点(Start Vertex)到结束顶点(End Vertex)的最短路径(Simple Path)的算法。
def findShortestPath(graph,start,end,path=[]):
path = path +[start]
if start == end:
return path
shortestPath = []
for node in graph[start]:
if node not in path:
newpath = findShortestPath(graph,node,end,path)
if newpath:
if not shortestPath or len(newpath)<len(shortestPath):
shortestPath = newpath测试代码如下:
g = { "a" : ["d"],
"b" : ["c"],
"c" : ["b", "c", "d", "e"],
"d" : ["a", "c"],
"e" : ["c"],
"f" : []
}
graph = Graph(g)
print('The path from vertex "a" to vertex "b":')
path = graph.find_path("a", "b")
print(path)
print('All paths from vertex "a" to vertex "b":')
path = graph.find_all_paths("a", "b")
print(path)路径查找的结果如下:
The path from vertex "a" to vertex "b": ['a', 'd', 'c', 'b']
All paths from vertex "a" to vertex "b":
[['a', 'd', 'c', 'b'], ['a', 'f', 'd', 'c', 'b']]3.2 Graph路径查找的非递归实现
Graph中查询最短路径的非递归遍历算法利用Queue的先进先出的特性,以起点Node为中心,波浪式的向外查找,直至找到目标Node。这种波浪式的查找方法,保证了找到的一定是起点Node到终点Node的最短路径。在查找过程中,记录了查询路径上所有Node的前驱节点,从而保证了在查到目标节点之后能够追溯到完整的路径。

Python的实现代码如下:
def extractPath(self, u, pred):
path = []
k = u
path.append(k)
while k in pred:
path.append(pred[k])
k = pred[k]
path.reverse()
return path
def findShortestPath(self, start, end, path=[]):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
closed = set()
# Create a queue for BFS
opened = []
pred = {}
# Mark the source node as visited and enqueue it
opened.append(start)
closed.add(start)
while opened:
u = opened.pop(0)
if u == end:
path = self.extractPath(u, pred)
return path
for i in self.__graph_dict:
if i not in closed:
opened.append(i)
pred = u
closed.add(i)测试代码如下:
g = { "a" : ["d"],
"b" : ["c"],
"c" : ["b", "c", "d", "e"],
"d" : ["a", "c"],
"e" : ["c"],
"f" : []
}
graph = Graph(g)
print('The path from vertex "a" to vertex "b":')
path = graph.findShortestPath("a", "b")
print(path)输出最短路径:
The path from vertex "a" to vertex "b":
['a', 'd', 'c', 'b']4、Mission Planner的路径规划
目前为止,我们已经知道,在路径规划技术中,首先将地图构建为Node-Edge的Graph结构,然后基于Graph和BFS算法实现从起始Node和目的地Node的路径查找。但是,我们必须知道到,本文介绍的路径规划是Graph的所有Edge权重是完全相等,这是不符合实际情况的,实际的工程应用的路径规划要更为复杂,要考虑到道路交通状况、路径长度、到达时间、乘客上下车位置等等,每个Edge都会赋予不同的权重,不同的权重表达了该Edge被选中的可能性。后面我们将继续学习在有权重的Graph中如何实现路径查找。
参考链接
1、Graphs in Python
2、Coursera多伦多大学自动驾驶课程-Motion Planning for Self-Driving Cars
注:本文首发于微信公众号,转载请注明出处,谢谢!

公众号:半杯茶的小酒杯
个人博客地址:
推荐阅读: |
|