|
|
一、开篇
其实这篇blog一周前就应该写的,可惜被上一篇blog霸占了。但是也不算晚,整理了很多算法基础知识,使得本篇blog更充实。一人之力总是有限的, 难免有不足之处,大家见谅,有写的不好的地方劳烦指正。看到标题了吧,属于连载篇,所以后续还会有相关问题的补充的。
二、版权声明
博主:summer
声明:喝水不忘挖井人,转载请注明出处。
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_21842557
联系方式:dxl0725@126.com
技术交流QQ:1073811738
三、实验平台
Software Version:PX4Firmware
Hardware Version:pixhawk
IDE:eclipse Juno (Windows)
四、基础知识
1、写在前面
无人机控制部分主要分为两个部分,姿态控制部分和位置控制部分;位置控制可用远程遥控控制,而姿态控制一般由无人机系统自动完成。姿态控制是非常重要的,因为无人机的位置变化都是由姿态变化引起的。
下图阐释了PX4源码中的两个环路控制,分为姿态控制和位置控制。
补充:关于Pixhawk原生固件中姿态(估计/控制)和位置(估计/控制)源码的应用问题
PX4Fireware原生固件中的modules中姿态估计有多种:Attitude_estimator_ekf、Attitude_estimator_q、ekf_att_pos_estimator。
位置估计有:ekf_att_pos_estimator、local_position_estimator、position_estimator_inav
姿态控制有:fw_att_control、mc_att_control、mc_att_control_multiplatform、vtol_att_control
位置控制有:fw_pos_control_l1、fw_pos_control_l1、mc_pos_control_multiplatform
四旋翼用到以上哪些估计和控制算法呢?这部分在启动代码rc.mc_app里面有详细的说明。

默认的是:
姿态估计 Attitude_estimator_q
位置估计 position_estimator_inav
姿态控制 mc_att_control
位置控制 mc_pos_control
2、飞行控制(该部分属于理论概述)
飞行控制分为姿态控制和位置控制,该文章主讲姿态控制。
所谓姿态控制,主要就是在前期姿态解算的基础上对四旋翼飞行器进行有效的飞行控制,以达到所需要的控制效果。在这种情况下,算法要学会如何连续地做决策,并且算法的评价应该根据其所做选择的长期质量来进行。举一个具体的例子,想想无人机飞行所面临的难题:每不到一秒,算法都必须反复地选择最佳的行动控制。控制过程还是以经典的PID反馈控制器为主(在控制环路中可以添加smith预测器)。那么如何实现控制呢?
以四旋翼飞行器为例,主要就是通过改变旋翼的角速度来控制四旋翼无人机。每个旋翼产生一个推力(F1、F2、F3、F4)和一个力矩,其共同作用构成四旋翼无人机的主推力、偏航力矩、俯仰力矩和滚转力矩。在四旋翼无人机中,正对的一对旋翼旋转方向一致,另外一对与之相反,来抵消静态平稳飞行时的回转效应和气动力矩。升降以及RPY的实现不在赘述。控制对象就是四旋翼无人机,其动力学模型可以描述为:将其视为有一个力和三个力矩的三维刚体。如下给出了小角度变化条件下的四旋翼无人机的近似动力学模型:
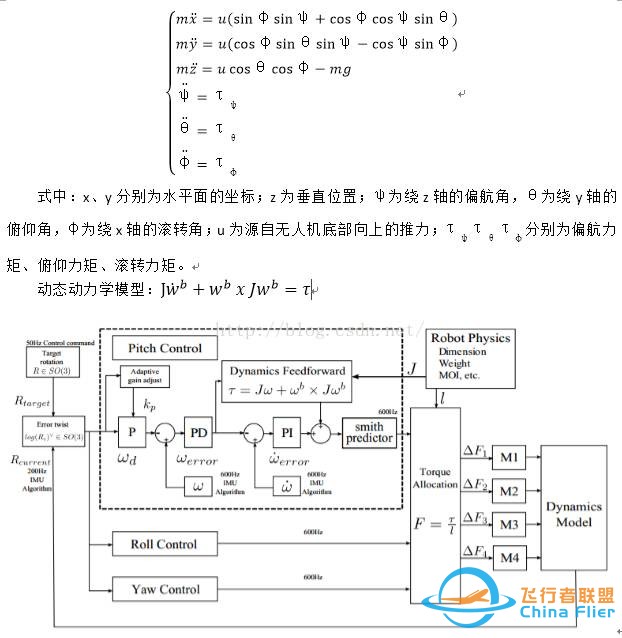
PS:PX4的姿态控制部分使用的是roll-pitch和yaw分开控制的(是为了解耦控制行为),即tilt和torsion两个环节。感性认识一下,如下图:
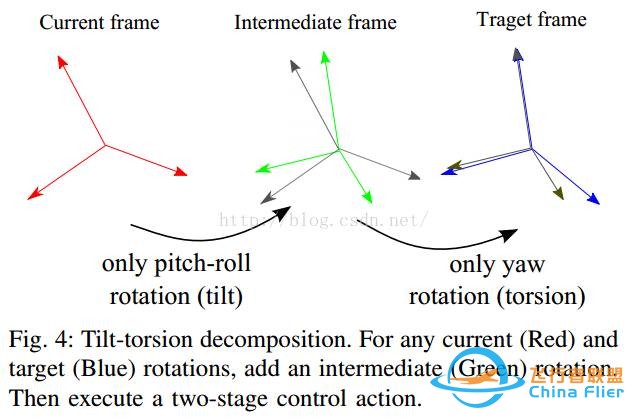
根据经验所得,控制toll-pitch比控制yaw更容易实现。比如同样是实现10°的变化,roll-pitch需要60ms左右;但是yaw控制器却需要接近150ms。(上面两幅图是出自DJI某哥写的论文里面,仅作参考,结合理解Pixhawk)
控制流程:
1)、预处理:各参数的初始化。
2)、稳定roll-pitch的角速度。
3)、稳定roll-pitch的角度。
4)、稳定yaw的角速度。
5)、稳定yaw的角度。
其中在第五步中有一个yaw的前馈控制(MC_YAW_FF):There is MC_YAW_FF parameter that controls how much of userinput need to feed forward to yaw rate controller. 0 means very slow control,controller will start to move yaw only when sees yaw position error, 1 meansvery fast responsive control, but with some overshot, controller will move yawimmediately, always keeping yaw error near zero。This parameter is not critical and can be tuned in flight, inworst case yaw responce will be sluggish or too fast. Play with FF parameter toget comfortable responce. Valid range is 0…1. Typical value is 0.8…0.9. (Foraerial video optimal value may be much smaller to get smooth responce.) Yawovershot should be not more than 2-5%。
摘自:
https://pixhawk.org/users/multirotor_pid_tuning
3、 进入姿态控制源码的前期过程
首先感性认识一下姿态控制部分的框架,控制部分分为内外环控制,内环控制角速度、外环控制角度。控制过程是先根据目标姿态(target)和当前姿态(current)求出偏差角,然后通过角速度来修正这个偏差角,最终到达目标姿态。
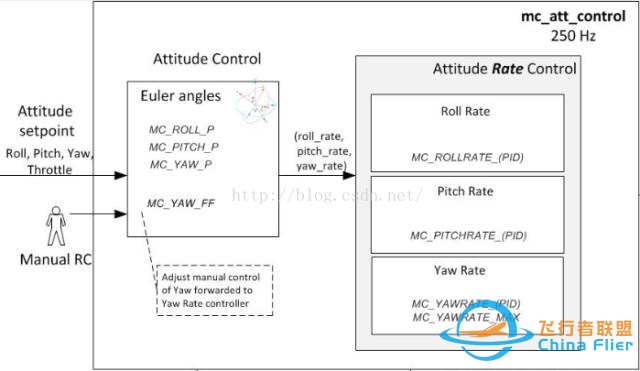
和姿态解算算法的流程几乎类似,主要的代码流程首先就是按照C++语言的格式引用C语言的main函数,但是在该处变成了:
extern "C" __EXPORT int mc_att_control_main(int argc, char *argv[])。
然后:跳转到所谓的main函数,该部分有个要注意的点,如下代码所示:即mc_att_control::g_control = new MulticopterAttitudeControl;//重点(934),new关键词应该不陌生吧,类似于C语言中的malloc,对变量进行内存分配的,即对姿态控制过程中使用到的变量赋初值。
int mc_att_control_main(int argc, char *argv[]){ if (argc < 2) { warnx("usage: mc_att_control {start|stop|status}"); return 1; } if (!strcmp(argv[1], "start")) { if (mc_att_control::g_control != nullptr) { warnx("already running"); return 1; } mc_att_control::g_control = new MulticopterAttitudeControl;//重点 if (mc_att_control::g_control == nullptr) { warnx("alloc failed"); return 1; } if (OK != mc_att_control::g_control->start()) {//跳转 delete mc_att_control::g_control; mc_att_control::g_control = nullptr; warnx("start failed"); return 1; } return 0; }
然后捏:start函数
Int MulticopterAttitudeControl::start(){ ASSERT(_control_task == -1); /* start the task */ _control_task = px4_task_spawn_cmd("mc_att_control", SCHED_DEFAULT, SCHED_PRIORITY_MAX - 5, 1500,(px4_main_t)&MulticopterAttitudeControl::task_main_trampoline, nullptr); if (_control_task < 0) { warn("task start failed"); return -errno; } return OK;}
其中上面有个封装了nuttx自带的生成task的任务创建函数(他把优先级什么的做了重新的define,这么做是便于代码阅读):px4_task_spawn_cmd(),注意它的用法。其函数原型是:
px4_task_t px4_task_spawn_cmd(const char *name, int scheduler, int priority, int stack_size, px4_main_t entry, char *const argv[])
第一个参数是namespace,第二个参数是选择调度策略,第三个是任务优先级,第四个是任务的栈空间大小,第五个是任务的入口函数,最后一个一般是null。
然后捏:
Void MulticopterAttitudeControl::task_main_trampoline(int argc, char *argv[]){ mc_att_control::g_control->task_main();}
再然后捏:终于到本体了。
Void MulticopterAttitudeControl::task_main(){}
比较讨厌的就是为什么要封装那么多层,应该是水平不够,还没有理解此处的用意。下面就是重点了。
五、重点
1、姿态控制源码_订阅
姿态控制的代码比姿态解算的代码少了不少,所以接下来分析应该会比较快。
首先还是需要通过IPC模型uORB进行订阅所需要的数据。需要注意的一个细节就是在该算法处理过程中的有效数据的用途问题,最后处理过的数据最后又被改进程自己订阅了,然后再处理,再订阅,一直处于循环状态,这就是所谓的PID反馈控制器吧,最终达到所需求的控制效果,达到控制效果以后就把一系列的控制量置0(类似于idle),该任务一直在运行,随启动脚本启动的。
/* * do subscriptions */ _v_att_sp_sub = orb_subscribe(ORB_ID(vehicle_attitude_setpoint)); _v_rates_sp_sub = orb_subscribe(ORB_ID(vehicle_rates_setpoint)); _ctrl_state_sub = orb_subscribe(ORB_ID(control_state)); _v_control_mode_sub = orb_subscribe(ORB_ID(vehicle_control_mode)); _params_sub = orb_subscribe(ORB_ID(parameter_update)); _manual_control_sp_sub = orb_subscribe(ORB_ID(manual_control_setpoint)); _armed_sub = orb_subscribe(ORB_ID(actuator_armed)); _vehicle_status_sub = orb_subscribe(ORB_ID(vehicle_status)); _motor_limits_sub = orb_subscribe(ORB_ID(multirotor_motor_limits));
上面这些订阅到底订阅了哪些东西呢,顾名思义,根据ORB()中的参数的名称就是知道订阅的到底用于做什么的了。这套开源代码中最优越的地方时变量的命名很好,通俗易懂。
2、 参数初始化
紧随上面的代码就是参数数据的获取,parameters主要就是我们前期定义的感兴趣的数据,在姿态控制中的这些数据都是私有数据(private), 比如roll、pitch、yaw以及与它们对应的PID参数。注意区分_params_handles和_params这两种数据结构(struct类 型)。
/* initialize parameters cache */ parameters_update();函数原型欣赏:int MulticopterAttitudeControl::parameters_update(){ float v; /* roll gains */ param_get(_params_handles.roll_p, &v); _params.att_p(0) = v; param_get(_params_handles.roll_rate_p, &v); _params.rate_p(0) = v; param_get(_params_handles.roll_rate_i, &v); _params.rate_i(0) = v; param_get(_params_handles.roll_rate_d, &v); _params.rate_d(0) = v; param_get(_params_handles.roll_rate_ff, &v); _params.rate_ff(0) = v; /* pitch gains */ 省略 /* yaw gains */ 省略 /* angular rate limits */ param_get(_params_handles.roll_rate_max, &_params.roll_rate_max); _params.mc_rate_max(0) = math::radians(_params.roll_rate_max); param_get(_params_handles.pitch_rate_max, &_params.pitch_rate_max); _params.mc_rate_max(1) = math::radians(_params.pitch_rate_max); param_get(_params_handles.yaw_rate_max, &_params.yaw_rate_max); _params.mc_rate_max(2) = math::radians(_params.yaw_rate_max); /* manual rate control scale and auto mode roll/pitch rate limits */ param_get(_params_handles.acro_roll_max, &v); _params.acro_rate_max(0) = math::radians(v); param_get(_params_handles.acro_pitch_max, &v); _params.acro_rate_max(1) = math::radians(v); param_get(_params_handles.acro_yaw_max, &v); _params.acro_rate_max(2) = math::radians(v); /* stick deflection needed in rattitude mode to control rates not angles */ param_get(_params_handles.rattitude_thres, &_params.rattitude_thres); _actuators_0_circuit_breaker_enabled = circuit_breaker_enabled("CBRK_RATE_CTRL", CBRK_RATE_CTRL_KEY); return OK;}
重点分析一下上述代码:其中param_get()函数比较重要,特别是内部使用的lock和unlock的使用(主要就是通过sem信号量控制对某一数据的互斥访问)。
Int param_get(param_t param, void *val){ int result = -1; param_lock(); const void *v = param_get_value_ptr(param); if (val != NULL) { memcpy(val, v, param_size(param)); result = 0; } param_unlock(); return result;}
上述使用的*lock和*unlock通过sem实现互斥访问(进临界区),源码如下。
/** lock the parameter store */static void param_lock(void){ //do {} while (px4_sem_wait(¶m_sem) != 0);}/** unlock the parameter store */static void param_unlock(void){ //px4_sem_post(¶m_sem);}
上面是开源代码中的,代码里面把lock和unlock函数都写成空函数了,那还有屁用啊。应该是由于程序开发和版本控制不是一个人,有的程序开发到一半人走了,搞版本控制的,又找不到新的人来进行开发,搁置了忘记修改回来了吧;再或者别的什么意图。
经过上述分析,该parameters_update()函数主要就是获取roll、pitch、yaw的PID参数的。并对三种飞行模式(stablize、auto、acro)下的最大姿态速度做了限制。
3、NuttX任务使能
/* wakeup source: vehicle attitude */ px4_pollfd_struct_t fds[1]; fds[0].fd = _ctrl_state_sub; fds[0].events = POLLIN;
注意上面的fd的赋值。随后进入任务的循环函数:while (!_task_should_exit){}。都是一样的模式,在姿态解算时也是使用的该种方式。
4、阻塞等待数据
/* wait for up to 100ms for data */ int pret = px4_poll(&fds[0], (sizeof(fds) / sizeof(fds[0])), 100); /* timed out - periodic check for _task_should_exit */ if (pret == 0) { continue; } /* this is undesirable but not much we can do - might want to flag unhappy status */ if (pret < 0) { warn("mc att ctrl: poll error %d, %d", pret, errno); /* sleep a bit before next try */ usleep(100000); continue; } perf_begin(_loop_perf);
首先是px4_poll()配置阻塞时间100ms(uORB模型的函数API)。然后是打开MAVLINK协议,记录数据。如果poll失败,直接使用 关键词continue从头开始运行(注意while和continue的组合使用)。其中的usleep(10000)函数属于线程级睡眠函数,使当前线程挂起。原文解释为:
“Theusleep() function will cause the calling thread to be suspended from executionuntil either the number of real-time microseconds specified by the argument'usec' has elapsed or a signal is delivered to the calling thread。”
上面最后一个perf_begin(_loop_perf),是一个空函数,带perf开头的都是空函数,它的作用主要是“Empty function calls forroscompatibility”。
5、重点来了(获取当前姿态Current)
终于到了姿态控制器了,兴奋不?别只顾着兴奋了,好好理解一下。尤其是下面的几个*poll函数,特别重要,后期算法中的很多数据都是通过这个几 个*poll()函数获取的,也是uORB模型,不理解这个后去会很晕的,别说没提醒啊;代码中没有一点冗余的部分,每一个函数、每一行都是其意义所在。
/* run controller on attitude changes */ if (fds[0].revents & POLLIN) { static uint64_t last_run = 0; float dt = (hrt_absolute_time() - last_run) / 1000000.0f; last_run = hrt_absolute_time(); /* guard against too small (<2ms) and too large (>20ms) dt's */ if (dt < 0.002f) { dt = 0.002f; } else if (dt > 0.02f) { dt = 0.02f; } /* copy attitude and control state topics *///获取当前姿态数据 orb_copy(ORB_ID(control_state), _ctrl_state_sub, &_ctrl_state); /* check for updates in other topics */ parameter_update_poll(); vehicle_control_mode_poll(); arming_status_poll(); vehicle_manual_poll(); vehicle_status_poll(); vehicle_motor_limits_poll();
注意上面的revents,要与events区分开来,两者的区别如下:
pollevent_t events; /* The input event flags */
pollevent_t revents; /* The output event flags */
首先就是判断姿态控制器的控制任务是否已经使能,然后就是检测通过hrt获取时间精度的所需时间,并且约束在2ms至20ms以内。完了,orb_copy()函数怎么用的忘记了。。。。
/** * Fetch data from a topic.* This is the only operation that will reset the internal marker that * indicates that a topic has been updated for a subscriber. Once poll * or check return indicating that an updaet is available, this call * must be used to update the subscription.* @param meta The uORB metadata (usually from the ORB_ID() macro) * for the topic. * @param handle A handle returned from orb_subscribe. * @param buffer Pointer to the buffer receiving the data, or NULL * if the caller wants to clear the updated flag without * using the data. * @return OK on success, ERROR otherwise with errno set accordingly. */int orb_copy(const struct orb_metadata *meta, int handle, void *buffer){ return uORB::Manager::get_instance()->orb_copy(meta, handle, buffer);}
第三个参数就是为了保存通过orb_subscribe()函数订阅获得的有效数据,该部分获取的是_ctrl_state,即控制姿态的数据,数据结构如下:(包含三轴加速度、三轴速度、三轴位置、空速、四元数、roll/pitch/yaw的速率)。记住这个copy的内容,后面会用到多次。
然后就是检测数据是否已经更新,举一例说明问题。
/* check for updates in other topics */parameter_update_poll();vehicle_status_poll();//注意这个,后面会用到内部的数据处理结果,即发布和订阅的ID问题。
函数原型:
Void MulticopterAttitudeControl::parameter_update_poll(){ bool updated; /* Check if parameters have changed */ orb_check(_params_sub, &updated); if (updated) { struct parameter_update_s param_update; orb_copy(ORB_ID(parameter_update), _params_sub, ¶m_update); parameters_update(); }}
然后捏:飞行模式判断是否是MAIN_STATE_RATTITUD模式,该模式是一种新的飞行模式,只控制角速度,不控制角度,俗称半自稳模式(小舵量自稳大舵量手动),主要用在setpoint中,航点飞行。根据介绍,这个模式只有在pitch和roll都设置为Rattitude模式时才有意义,如果yaw也设置了该模式,那么就会自动被手动模式替代了。所以代码中只做了x、y阈值的检测。官方介绍:
RATTITUDE The pilot's inputs are passed as roll, pitch, and yaw rate commands to the autopilot if they are greater than the mode's threshold. If not the inputs are passed as roll and pitch angle commands and a yaw rate command. Throttle is passed directly to the output mixer.
/* Check if we are in rattitude(新的飞行模式,角速度模式,没有角度控制) mode and the pilot is above the threshold on pitch or roll (yaw can rotate 360 in normal att control). If both are true don't even bother running the attitude controllers */if(_vehicle_status.main_state == vehicle_status_s::MAIN_STATE_RATTITUDE){ if (fabsf(_manual_control_sp.y) > _params.rattitude_thres || fabsf(_manual_control_sp.x) > _params.rattitude_thres){ _v_control_mode.flag_control_attitude_enabled = false; } }

来源:无人机
如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,请分享给您的朋友
分享知识,分享快乐
关注前沿科技一点通:了解更多前沿科技
|
|